What is Gout? causes, symptoms, diagnosing, treatment, how to prevent Gout
The post will help you understand more about the disease about what is gout, treatments, and preventions.
-
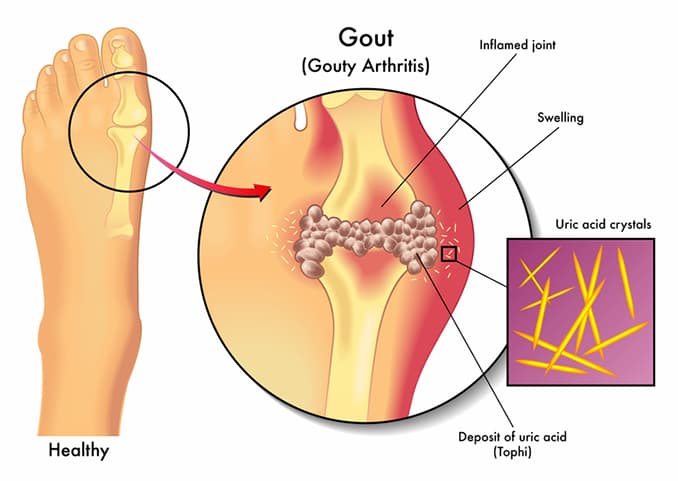
What is Gout?
Gout is arthritis and frequent in men. The majority of Gout patients is diagnosed as middle-aged men with age from 40-50 account for 95% of those who are at high risk for obesity, alcoholism, coffee, and people with a family history of illness gout. There are only a small proportion of female patient’s accounts for about 5% which usually occur after menopause.
-
What causes gout?
The underlying cause of Gout lies in genetic problems. So far, scientists have identified five genes involved in Gout including HGPRT1, Glc6-phosphate in the liver, and three PRPPs 1, 2, 3 in the testes. Specifically, the following principal reasons can be cited
– Diets rich in purines cause Gout
This is considered to be the leading cause, the most obvious and direct effect that has led to an increase in Gout. In addition, many people especially men like to eat meat which has a lot of purines. Furthermore, according to statistics, up to 85% of people with gout have a history of alcohol use continuously at least five years before.
– Due to the habit of non-scientific activities
Many people said that Gout is the disease spending only for rich people because they eat a lot of meat as well as foods with high protein. However, one of the primary causes of Gout stays in the habit of non-scientific activities. If you often work hard, or sweat but not drink enough, you can have gout as well. This causes large amounts of uric acid to accumulate in the bloodstream instead of being diluted and excreted and until the excess is allowed to form Gout.
In short, Gout is a disease of the purine metabolism that results in hyperuricemia, which results in the deposition of urinary crystals in arthritic joints that can occur in any of the subjects.
-
Symptoms of Gout
Patients with Gout at the first stage usually do not have any symptoms excepting for elevated blood uric acid levels which mean that they must be tested. The characteristic clinical manifestations are generally one or more of the joints of the patient that will be the swollen, hot, red and severe pain. Furthermore, pain occurs after you collide, impact on the pain or after meals and partying with drinking lots of alcohol.
Joints are more prone to pain when you have gout. These are joints in the ankles, feet, knees, wrists, elbows and small joints of the hands, even in small joints around the body. At this stage, depending on the state and lifestyle of the patients, the pain will relapse within several years in each person. Usually, it will relapse from 1 to 3 years. The worry, however, is that most of these people when treated with pain, think they have recovered from the disease without knowing that the disease is progressing silently.
However, unless treated further and thoroughly, in the later stages of Gout, acute pain causes joint damage, resulting in loss of movement, the formation of chronic pain and accumulation of tops causing joint deformities can even lead to disability.
-
Diagnosing Gout
As mention, the clinical method is to diagnose Gout and to seek crystals of Urat salts under the microscope. If you want to try the usual way to identify patients with the first Gout attack, you can drink Colchicine. If after a few hours you have had pain, you have gout.
However, you should note that during acute Gout attacks, uric acid levels may be normal but it is not necessarily elevated. Therefore, to eliminate acute Gout diagnosis, you can not use blood test. However, you can still monitor the effectiveness of the treatment by monitoring blood uric acid levels, if blood levels of Urate are reduced.
-
Treatment of Gout
There is a harsh reality that when you suffer from gout, you will suffer from acute pain whether to take medication or not to take medication. Therefore, the goal of treating Gout first is to help the patient relieve pain while at the same time keeping the distance between gout attacks long.
In long-term, the treatment of Gout will prevent the pain at other positions of the patient’s body at the same time and minimize the formation of kidney stones and tumors under the skin around gout. When you successfully treat Gout, the discomfort caused by Gout symptoms will diminish considerably and decrease the long-term damage in gout joints. However, there are still chronic patients with Gout which are associated with some other debilitating conditions including kidney failure, liver failure, and fluid retention. The use of drugs to treat these diseases uncontrollably will make Gout more severe.
-
How to prevent Gout
From the causes of Gout, you may find that to the way to avoid this disease; you need to eat healthy and regular sports activities, avoid overweight obesity and so on. Studies also show that when weight loss can reduce uric acid levels and reduce the occurrence of acute Gout attacks. If you are addicted to alcohol, you should decrease or stop altogether because drinking a lot of beer or spirits increases your risk of Gout.
Moreover, you should drink at least 2-3 liters of water a day as it removes uric acid in the body through the urinary tract. Also, at age 30 or older, you should avoid sudden changes in your body, shocking your body as if it were hot, cold water, etc. because they could be the cause of your metabolism.
Besides that, you should avoid the foods which have high purines such as anchovy, sardines, geese, etc. You also should reduce meat in your meals and increase to eat vegetables and fruits.
Hope that the post above will help you understand more about the disease about treatment and prevention. If you need more information, you should contact with the doctor to get more.
See more:
1- What is lactose intolerance? symptoms, cause, treatment, how to prevent
2- What is irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)? Causes, Treatments
3- What is a sinus infection? symptoms, cause, treat, prevent the sinus infection
4- What is chronic fatigue syndrome? Symptoms, causes, risks, treatment, prevent
5- What is strep throat? symptoms, causes, treatments, diagnose, prevent
6- What is Lyme disease? Symptoms – Diagnosis – Treatment – Prevent
7- What is pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)? Causes – Signs – How to treat – How to prevent
8- What is polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)? Signs – The main cause – Treat
9- What is diabetes? Types – Symptoms – Complications of diabetes