What is polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)? Signs – The main cause – Treat
Useful information about polycystic ovary syndrome
Do you hear about polycystic ovary syndrome? The post will help you understand more about the disease.
-
What is polycystic ovary syndrome?
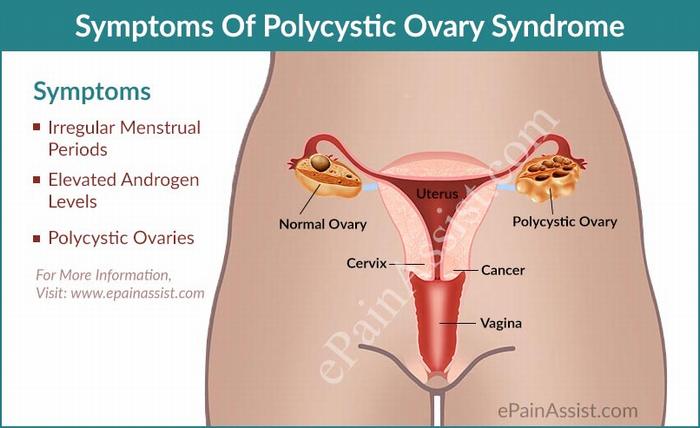
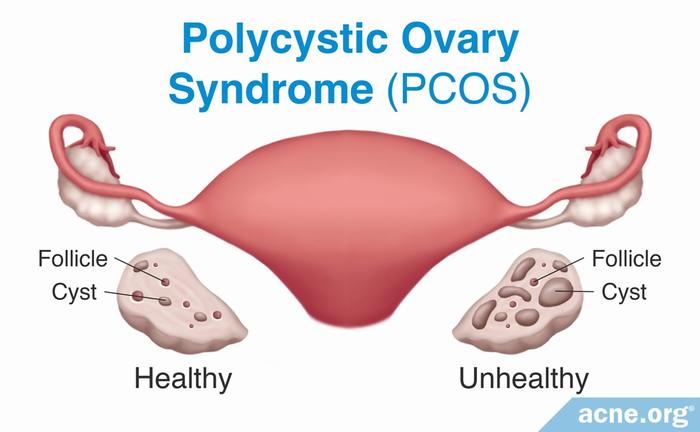
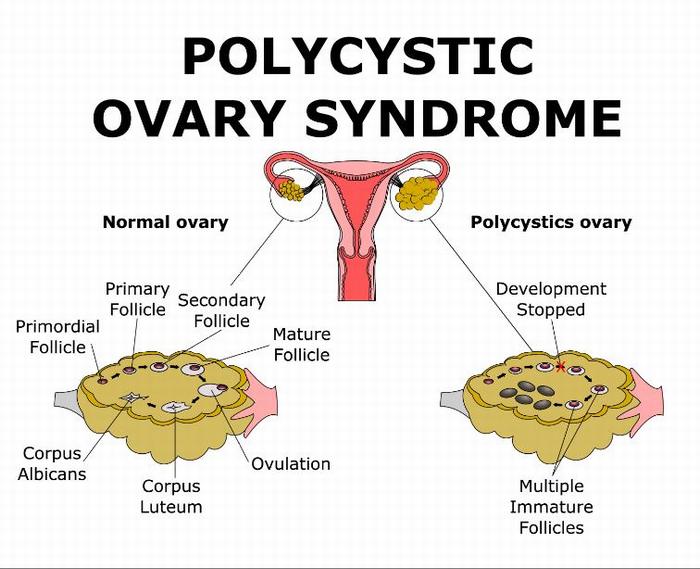
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a disease that occurs in women with too many male hormones while female hormones in the body are not sufficient. This makes the ovulation more abnormal; therefore, if you do not treat prematurely, hormonal imbalances can have serious health effects and increases the risk of certain diseases including diabetes, heart disease, and reproductive disorders. Furthermore, when women have polycystic ovary syndrome, the amount of male hormone in the body is too much to stop the ovulation causing the egg to fill up in the follicle. If the follicles do not develop normally, ovulation occurs incorrectly in the cycle which will lead to the imbalance of male and female hormones in the body.
Besides, most women have polycystic ovary disease, their body responds to insulin resistance preventing glucose metabolism. Therefore, the main treatment is carried out by the addition of insulin to bring glucose into the cell of the patient to provide energy to the body. However, if the body contains too much insulin, women are more likely to have the appetite, resulting in weight gain and the production of the hormone male.
-
Signs of polycystic ovary
Due to the different changing hormonal, the signs of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) also differ in women. Up to 80% of women with this syndrome are obese, overweight, and more than 70% of women have extensive hair growth in some part of their bodies such as the face, chest, lower abdomen, back or thighs. However, the post will show eight common signs of polycystic ovary syndrome.
– Irregular or prolonged menstrual cycles are the most common signs of polycystic ovaries. For example, in one year, you will have fewer than 9 “red lights” appearances. Each cycle lasts more than 35 days and abnormal bleeding. Menstruation is very rare or very much.
– Having difficulty conceiving
– Have skin problems such as acne, dark patches of skin or excess skin in the armpits or around the neck.
– Sleep apnea
– Grow feathers on the face, on the chest, abdomen, back or thighs.
– Depression or mood swings.
– Weight gain and obesity.
– Thin hair or heavy hair loss.
-
The main cause of polycystic ovaries
According to scientists, the following factors may be the cause of polycystic ovary syndrome
– Genetic
This is the highest risk factor for polycystic ovary syndrome. If your mother, sister or young sister has a polycystic ovary, you will have a higher risk of developing this disease or have diabetes or irregular menstrual cycles. Researchers also think the possibility that certain genes may be associated with polycystic ovary syndrome.
– Insulin resistance or metabolic syndrome
Insulin is known as an important hormone that helps control glucose in the body and converting blood sugar into cells. Therefore, if your body is insulin resistant, it means the tissues in the body are resistant to the effects of insulin. This inadvertently causes the ability to use insulin may be interrupted. Thus, the pancreas secretes more insulin to supply the cellular pathway. This excess of insulin can affect the ovaries by increasing the production of androgens which may interfere with the growth of the follicle, reducing the ovulation ability of the ovary, causing acne and hair loss. Besides, when glucose does not convert into cells, it will be converted to fat causes weight gain, obesity or difficult to lose weight.
– Diet
Many hypotheses show that diets with too much starch may also be responsible for the polycystic ovary syndrome. Most people with polycystic ovaries are overweight, but thin people are also at risk. Furthermore, the unbalanced body with obesity is characteristic of the metabolic syndrome caused by insulin resistance.
-
How to diagnose polycystic ovary syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome can be difficult to diagnose because the symptoms in each person will be different. However, if you have polycystic ovaries, symptoms may appear and disappear in a short time. Therefore, firstly, the doctor needs to rule out the possible causes of this symptom such as thyroid problems. Besides that, your doctor will diagnose you with polycystic ovary syndrome based on the following factors.
– History of your health and your menstrual cycle.
– Blood tests to measure hormone levels
– Ultrasound through the vagina to check whether the ovaries are polycystic and enlarged
-
How to treat polycystic ovary syndrome
Although polycystic ovarian syndrome can not be cured completely, you can cope with the symptoms. Depending on the needs of the patient, the doctor will give appropriate treatment regimens such as treatment to regulate the menstrual cycle or treatment for pregnancy.
- Use of fertility drugs
– Clomiphene: If you lose weight and your cycle is not regular, your doctor will prescribe clomiphene which is a medicine helping you to increase your fertility. About 80% of women treated with clomiphene start ovulation within the first three months. Among them, 30-40% women can pregnant in the third treatment.
– Letrozole: Many experts advise women to use letrozole to stimulate ovulation. Recent research shows that this drug is more effective than clomiphene in regulating ovulation and pregnancy support for women with polycystic ovary syndrome.
– Metformin: This is one of the drugs that stimulate ovulation. This drug will be more effective if combined with clomiphene or letrozole during the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome.
– Gonadotropins: If treatment with other drugs is not effective, your doctor will recommend gonadotropin. This is an injectable drug that stimulates ovulation as well as helps develop eggs. Up to 60% of women with polycystic ovary syndrome are pregnant when treated with this drug.
- Ovarian Surgery
If treatment with these drugs does not produce results, you can now choose a surgical procedure called ovarian drilling. Your doctor will perform surgery on your abdomen to make small holes in your ovaries. This helps to reduce levels of male hormones and enhance ovulation. Moreover, unlike oral or injectable drugs, ovarian drilling is a one-off treatment. The effect of this method is only temporary, but about 50% of pregnant women within one year of surgery.
- In Vitro Fertilisation
If there is no suitable treatment for you, IVF is considered the best method. First, the doctor will take the egg and sperm to carry out fertilization in the laboratory. Then they will put the embryo into your uterus so the embryo can develop into a fetus. The pregnancy rate depends on your age and fertility.
Sometimes the obstetrician or gynecologist will rely on your medical symptoms to indicate treatment options. It can even be referred to an endocrinologist.
Hopefully with the information provided by the article has helped you some knowledge about the benefits of polycystic ovary syndrome and understand the method that you are treating.
See more:
1- What is lactose intolerance? symptoms, cause, treatment, how to prevent
2- What is Gout? causes, symptoms, diagnosing, treatment, how to prevent Gout
3- What is a sinus infection? symptoms, cause, treat, prevent the sinus infection
4- What is chronic fatigue syndrome? Symptoms, causes, risks, treatment, prevent
5- What is strep throat? symptoms, causes, treatments, diagnose, prevent
6- What is Lyme disease? Symptoms – Diagnosis – Treatment – Prevent
7- What is pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)? Causes – Signs – How to treat – How to prevent
8- What is irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)? Causes, Treatments
9- What is diabetes? Types – Symptoms – Complications of diabetes