What is lactose intolerance? symptoms, cause, treatment, how to prevent
Things to know about lactose intolerance symptoms
If you are finding out information about lactose intolerance, you should read the post carefully because the post will show necessary and useful information about lactose intolerance.
-
What is lactose intolerance?
Lactose intolerance is a condition in which the body does not have enough lactase which is an enzyme in the small intestine to absorb lactose. Lactose is sugar in dairy products such as milk, cheese, etc. People who suffer from this disease when eating foods or drinks made from milk, the lactose in it will not break down will be transferred to the large intestine where the bacteria will break down lactose into liquid and gas. Therefore, it will cause the patient which will appear symptoms in the digestive system such as bloating, diarrhea. This lactose intolerance is usually not dangerous, but the symptoms of the disease often make you uncomfortable.
-
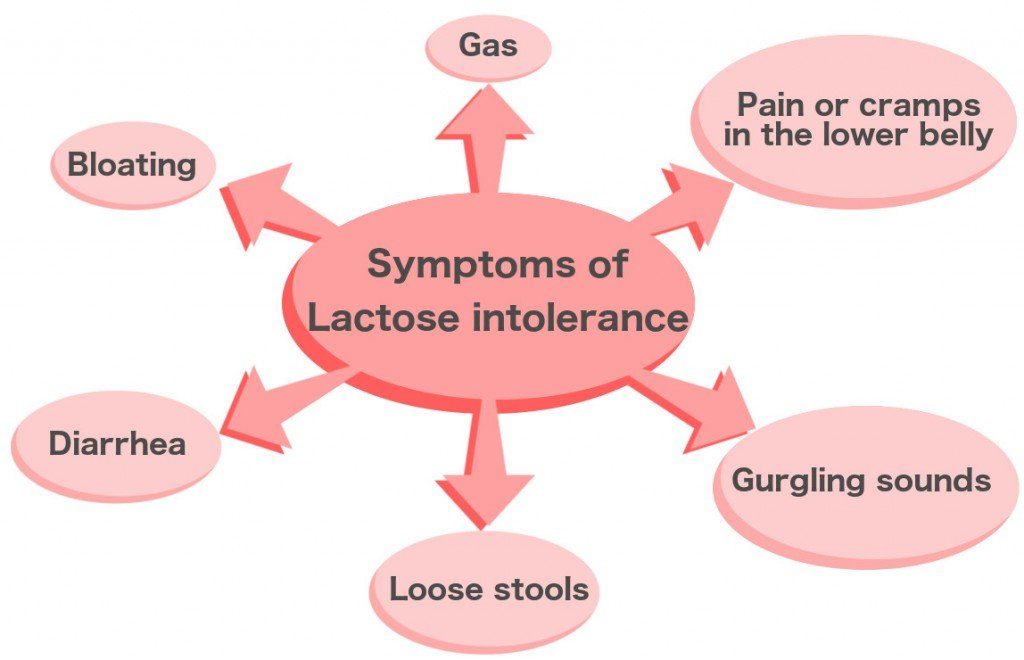
Lactose intolerance symptoms
Most lactose intolerance symptoms occur within half an hour to two hours after you eat dairy products including
– Stomach pain
– Cramp
– Full steam
– Nausea
– Diarrhea
Lactose intolerance symptoms in young children may be slightly different such as
– Diarrhea with bubbles
– Develops slowly
– Occasional vomiting
– Dermatitis due to diaper rash.
You may experience other symptoms and signs which are not mentioned. If you have any questions about the signs of the disease, you should consult your doctor.
Furthermore, if you have lactose intolerance symptoms which mentioned above after eating dairy products or have any questions or concerns, you should consult your doctor. Site and pathology may vary in many people. Moreover, you always talk to your doctor about the best diagnostic and treatment options available to you.
-
The cause lactose intolerance
The cause of lactose intolerance is that the body does not produce enough lactase enzyme to absorb lactose. For most people, the small intestine begins to produce less lactase after two years of age or after weaning. However, later patients can still eat dairy products without symptoms.
Digestive diseases such as Crohn’s disease and celiac disease which is a gastrointestinal disease that destroys the small intestine and obstructs the absorption of nutrients from the food, inflammation or trauma to the small intestine can reduce available lactase levels.
-
Risk of infection
Lactose intolerance is a fairly common disease. Anyone can get it, but most are African Americans, Asians and Mexican Americans. Most people with lactose intolerance can still control the condition without having to give up all dairy foods.
Factors that make you or your child lactose intolerant including
– Age. Lactose intolerance is more common in older adults and is less common in infants and young children
– Race. This disease is most common in blacks, Asians, Spanish, and Americans.
– Preterm birth. Babies with preterm delivery have the potential to reduce lactase levels as this enzyme increases in a late fetus in the third trimester.
– Diseases that affect the small intestine. Problems with the bowel can cause lactose intolerance including bacterial growth, Crohn’s disease or celiac disease.
– Some cures for cancer. If you receive radiation therapy to treat abdominal cancer or have had chemotherapy-related complications, your risk for lactose intolerance is higher.
-
How to treatment
To diagnose the disease, your doctor will ask you for a medical history and physical examination. Your doctor will also perform tests to measure lactose uptake in the digestive tract such as lactose intolerance, breathalyzed breath tests, and fecal acid testing for children. In case of unclear basis, the doctor will take a small tissue sample from the small intestine to study.
Infants and young children should not eat lactose-free foods. Adults and older children usually do not need to avoid lactose completely, but you should know the amount of lactose they can absorb based on the symptoms that appear. Calcium is essential for children, adolescents, pregnant women, lactating women or premenopausal women. Avoiding dairy products can make you lose calcium and vitamin D so you need to supplement them with calcium supplements or eat foods rich in calcium such as shrimp, broccoli, green leafy vegetables. Another way is to take lactase enzyme to improve lactose tolerance. Symptoms usually resolve after 3 weeks of discontinuation of dairy products.
-
How to prevent
You can control your condition if you notice a few things
– Revise your appointment to follow the progression of your symptoms as well as your state of health
– Listen to your doctor’s instructions, do not voluntarily take unprotected drugs or volunteer to quit smoking
– Talk to your doctor about the medicine you make because it may contain lactose
– Consider breastfeeding if you have a history of lactose intolerance
– Give your baby soy milk a substitute for regular milk
– Call your doctor if a non-dairy diet does not help to improve your symptoms
– Call your doctor if your baby is not gaining weight or having anorexia
Hope that the post will help you understand more about lactose intolerance. If you need more information about the disease, you should contact the doctor to know more.
See more:
1- What is irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)? Causes, Treatments
2- What is Gout? causes, symptoms, diagnosing, treatment, how to prevent Gout
3- What is a sinus infection? symptoms, cause, treat, prevent the sinus infection
4- What is chronic fatigue syndrome? Symptoms, causes, risks, treatment, prevent
5- What is strep throat? symptoms, causes, treatments, diagnose, prevent
6- What is Lyme disease? Symptoms – Diagnosis – Treatment – Prevent
7- What is pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)? Causes – Signs – How to treat – How to prevent
8- What is polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)? Signs – The main cause – Treat
9- What is diabetes? Types – Symptoms – Complications of diabetes